Are you near a AA battery? If so, pick it up and feel its weight. That’s roughly how much of the mineral magnesium you have in your body — about 25 grams, or a little less than an ounce. Magnesium has many health benefits, and plays a vital role in many bodily functions, yet it gets almost no press compared to its more famous buddies, iron and calcium.
While magnesium abounds in nature — it’s the seventh most common element on earth, by weight — we aren’t getting nearly enough of it to achieve and maintain optimal health. Somewhere between 10-30% of people worldwide — and around 50% of Americans — appear to be deficient. Magnesium deficiency is so common and widespread that it’s been called a public health crisis.
And compounding the problem is the fact that it’s hard to accurately measure magnesium levels in the body. Tests look at serum magnesium (in the blood) and not intracellular magnesium (the concentration of magnesium within cells, where it’s needed). It’s a little like trying to figure out the financial health of a bank by counting the money in the Brinks vans going to and from the building. There’s some relationship, but it’s far from the whole story.
But what exactly does magnesium do in your body? What are the health benefits of magnesium? And why are so many of us deficient these days? Read on to find out!
What is Magnesium?
Magnesium is a mineral needed to support a number of critical functions in your body. For instance, it helps maintain normal blood pressure, keeps your bones strong through the metabolism of calcium and potassium, and helps to keep your heartbeat steady. It’s a cofactor involved in over 300 enzyme systems that regulate biochemical reactions. And it’s a necessary component for energy production, DNA and RNA synthesis, and muscle and nerve function.
Magnesium is also an electrolyte, which means it carries an electric charge when dissolved in bodily fluids like blood. However, the majority of magnesium in your body is uncharged and is bound to proteins or stored in your skeleton. Approximately half of the magnesium in your body is found in bone, with very little circulating in blood. In fact, less than 1% of your body’s magnesium is in your bloodstream. And it remains very tightly controlled — primarily by your kidneys — which determine magnesium excretion or retainment.
6 Magnesium Health Benefits

Getting enough magnesium is not only essential for everyday physiological functioning. It plays a substantial role in the prevention of numerous health conditions, too. Below are some of the most researched magnesium health benefits.
1. Improved heart health
A 2017 meta-analysis of 11 studies published in Nutrition Journal concluded that magnesium levels circulating in the blood are inversely associated with the incidence of heart disease and hypertension. While more research is needed to determine optimal serum levels of magnesium, researchers were able to identify higher levels as having a protective effect on heart health. Specifically, for every 0.1 mmol/L increase in circulating magnesium, there was a 4% lower incidence of hypertension.
Furthermore, a 2005 study reviewed 20 randomized trials and found that administering intravenous or intramuscular magnesium prior to heart surgery was effective in preventing post-operative atrial fibrillation (AF), or irregular heartbeat. Blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other complications can result from AF.
In other research, magnesium supplementation has also been beneficial in lowering high blood pressure, especially among people with insulin resistance, prediabetes, and other high-risk groups.
2. Reduced risk for osteoporosis
Magnesium and calcium work together to keep your bones strong and healthy, so it makes sense that getting enough of these minerals can help slow or prevent skeletal weakening that often happens with age. A 2017 study published in the journal Nutrients examined associations between skeletal muscle mass, grip strength, bone density, and dietary magnesium among 156,575 men and women ages 39-72 from the UK Biobank cohort. The researchers found a significant association between magnesium intake and bone health. This suggests that getting enough magnesium in the diet could help maintain musculoskeletal health as you age and even prevent osteoporosis and bone fractures.
3. May help prevent type 2 diabetes
In addition to the link between magnesium and heart health, the 2017 meta-analysis mentioned above also found that higher circulating levels of magnesium were associated with a lower risk for developing type 2 diabetes. However, there has been no determination of optimal blood levels yet. A 2016 study published in Nutrients evaluated the dose-response relationship between magnesium intake and type 2 diabetes risk, looking at 25 studies, including 637,922 individuals, 26,828 of whom had the disease. After adjusting for BMI and age, the authors were able to identify a 8-13% reduction in risk for type 2 diabetes for every 100 mg/day increment of dietary magnesium intake.
4. May improve sleep patterns and quality
Magnesium is known to have a calming effect for many people, which may help improve sleep. This could have substantial health benefits, considering that an estimated 50% of older adults have some degree of insomnia, or difficulty sleeping at night. A 2012 study published in the Journal of Research in Medical Sciences found that 500 mg of supplemental magnesium, taken daily for eight weeks, resulted in subjectively improved sleep patterns among elderly individuals with insomnia, compared to a placebo group. Although total sleep time didn’t significantly differ between the two groups, those who received magnesium reported better sleep quality and less waking at night and early morning. In a 1998 study, a small group of older adults with insomnia were given 12.4 mmol of magnesium supplementation daily for four to six weeks. The study participants found that rates of restless leg syndrome decreased and that overall sleep efficiency improved.
5. May reduce and prevent migraines
A heavily studied health benefit of magnesium is the relationship between magnesium and migraines. Many researchers believe that magnesium deficiency may trigger waves of altered cortical activity, clumping of blood platelets in the brain, constricted blood vessels, and release of certain neurotransmitters that can lead to migraines. How much magnesium helps? Research on this is inconsistent, perhaps in part because not everyone has the same level of need. Some people suffering from migraine headaches have found that supplemental doses of up to 1000 mg of magnesium can alleviate their symptoms. But some people also find that doses that high can cause diarrhea or abdominal pain.
6. May help regulate mood
Getting enough magnesium may also help uplift your spirits. And some people use magnesium against depression. A 2017 study published in PLoS One aimed to determine if over-the-counter magnesium chloride supplementation improved symptoms among 126 adults in outpatient primary care clinics with reported mild-to-moderate depression. The participants received an intervention of 248 mg of magnesium per day for six weeks. And then, they underwent six weeks of no treatment as the control. Using the Patient Health Questionnaire-9, researchers found that magnesium supplementation resulted in significant improvement in depression scores. And 61% of the participants said they would continue using magnesium in the future.
How Much Magnesium Do You Need?

While a balanced diet that regularly includes magnesium-rich foods should meet your needs, most people in America don’t consume enough. Why? The modern industrialized diet — also known as the standard American diet (aptly acronymed as SAD) — is high in processed, packaged foods. And it tends to lack good, plant-based sources of magnesium.
So how much magnesium should you be aiming for? The Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDA) for magnesium are as follows:
- 0-6 months: 30 mg
- 7-12 months: 75 mg
- 1-3 years: 80 mg
- 4-8 years: 130 mg
- 9-13 years: 240 mg
- Boys 14-18 years: 410 mg
- Girls 14-18 years: 360 mg
- Men 19+ years: 400-420 mg
- Women 19+ years: 310-320 mg
- Pregnant teens: 400 mg
- Pregnant women: 350-360 mg
- Breastfeeding teens: 360 mg
- Breastfeeding women: 310-320 mg
Magnesium Deficiency

Scientific literature suggests that subclinical magnesium deficiency is rampant. And that it’s actually one of the leading causes of chronic disease — including cardiovascular disease and early mortality — around the globe. Subclinical magnesium deficiency indicates that your blood magnesium levels appear normal, but you still have an underlying mineral deficiency.
A USDA survey called “What We Eat in America” found that men take in under 350 mg of magnesium per day (when they should be getting 300-420 mg), while women average 260 mg when at least 310 mg would be optimal. Surveys show that men over the age of 70 and teenage girls tend to have the lowest magnesium consumption. On the other hand, combining dietary and supplemental magnesium typically exceeds minimum requirements.
Normal blood magnesium levels are between 0.75 and 0.95 mmol/L, which means magnesium deficiency occurs at levels under 0.75 mmol/L. Remember that less than 1% of your total body magnesium is in your blood, so when these levels are low, it could indicate that you have a more widespread deficiency.
What Causes Magnesium Deficiency?
In addition to inadequate consumption of magnesium from food, low magnesium levels in the body may be caused or worsened by:
- An excess of heavy metals due to soil contamination
- A lack of minerals due to soil erosion
- Having a digestive disorder, such as celiac disease or chronic diarrhea
- Having type 2 diabetes
- Being dependent upon alcohol
- Being elderly, as magnesium absorption decreases with age
- Taking certain medicines, including diuretics and proton-pump inhibitors, that can cause magnesium loss
Symptoms of early magnesium deficiency can include constipation, fatigue, loss of appetite, and weakness, which can eventually lead to more severe compilations. Some of these may be muscle contractions, seizures, low blood levels of calcium and potassium, abnormal heart rhythm, personality changes, and numbness in the limbs. Long-term, untreated magnesium deficiency can result in high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, osteoporosis, and heart disease.
Magnesium Overdose & Interactions
Overdosing on magnesium is really only possible if you’re taking supplements that contain the mineral. Dietary sources of magnesium are highly unlikely to result in toxic levels accumulating in your body, as your kidneys can typically filter out any excess.
Large doses of magnesium from dietary supplements or medications can cause diarrhea, nausea, and abdominal cramping. Diarrhea from magnesium happens because the unabsorbed salts in the intestine and colon stimulate gastric motility. In other words, magnesium makes things move pretty quickly through your intestinal tract. This is why magnesium is sometimes used to alleviate mild constipation. Magnesium carbonate, chloride, gluconate, and oxide are more likely to cause diarrhea.
Early signs of excessive magnesium intake can include low blood pressure, facial flushing, depression, urine retention, and fatigue. Eventually, if untreated, these symptoms can worsen and include muscle weakness, difficulty breathing, irregular heartbeat, and even, in very rare cases, cardiac arrest.
Extremely high doses can result in hypermagnesemia — or very high levels of magnesium in the bloodstream. Hypermagnesemia can become fatal, especially if your kidneys are not functioning optimally. Large doses of laxatives and antacids that contain magnesium may be a contributing factor to magnesium toxicity, typically when they’re providing over 5,000 mg of magnesium per day.
Lastly, magnesium supplements can interact with certain medications. For instance, bisphosphonates used to slow or prevent bone loss, antibiotics for bacterial infections, diuretics to promote water loss, or proton pump inhibitors often prescribed for management of acid reflux. Interactions may include excessive loss of magnesium, formation of insoluble complexes, and reduced efficacy of the medication.
Recommended Intake for Magnesium Supplements
How much magnesium is too much? There isn’t any known danger from eating too much magnesium from food. But there is a recommended upper intake level (UL), which clarifies the highest amount deemed safe to consume per day supplementally. Please note that this is in addition to your dietary magnesium.
- Birth to 12 months: None established
- 1–3 years: 65 mg
- 4–8 years: 110 mg
- 9–18 years, including pregnant or lactating women: 350 mg
- 19+ years, including pregnant or lactating women: 350 mg
Magnesium-Rich Foods
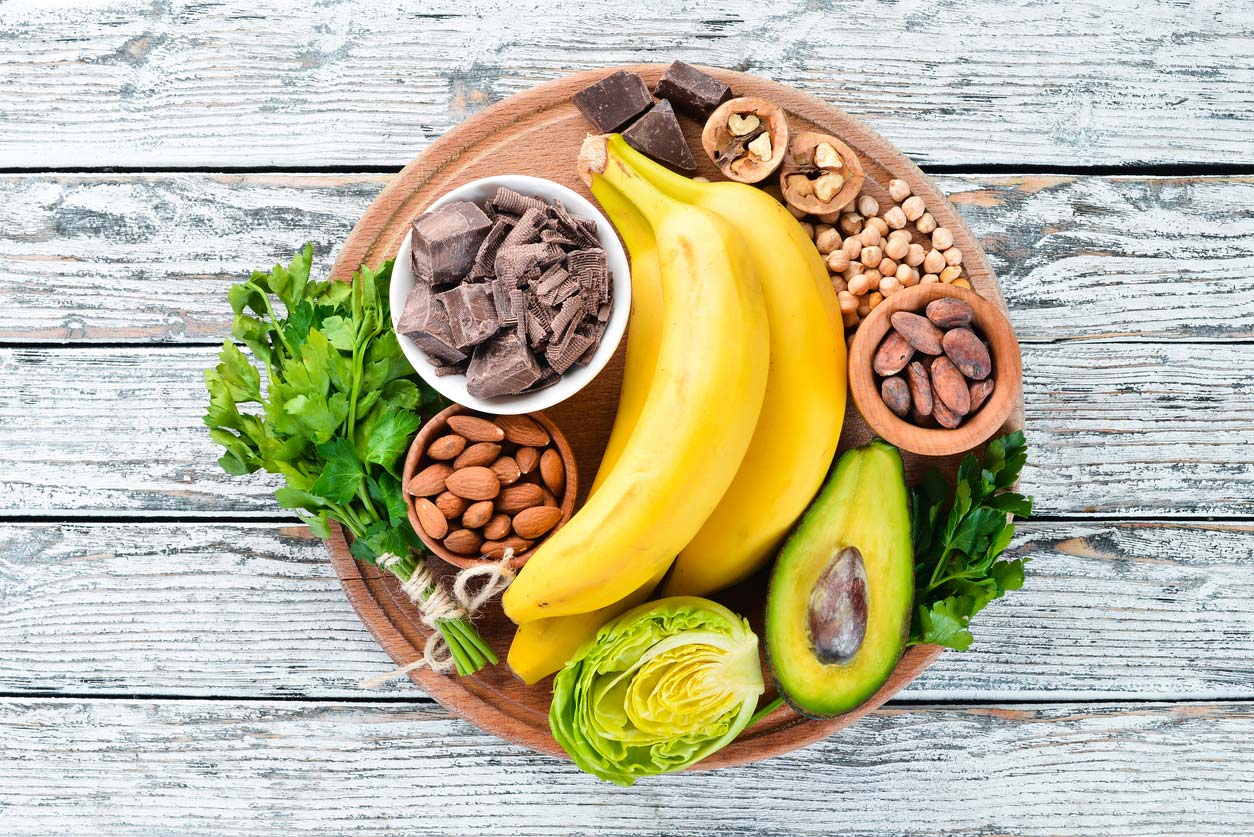

The best way to get magnesium in the right amount, and in a form your body can recognize and absorb efficiently, is through your diet.
Some of the best sources include:
- Nuts and seeds, especially almonds, cashews, and peanuts (technically a legume) — including nut butters made from them
- Spinach, especially when boiled
- Plant-based milks
- Beans and legumes, like black beans and edamame (soybeans)
- Dark chocolate, especially when you choose types that are at least 70% cacao or cocoa solids
- Avocado
- Potatoes
- Whole grains, especially quinoa and whole wheat flour
- Tofu and tempeh
- Bananas
- Cauliflower
There is little to no magnesium found in meat, eggs, or dairy products.
Magnesium Absorption

It’s important to get enough magnesium in your diet, but it’s also essential to do things that help your body absorb it well. Only about 30% to 40% of dietary magnesium is typically absorbed. So it’s helpful to know what you can do to keep that rate from dropping too much.
There could be several reasons for reduced magnesium absorption. The most common reason is that other nutrients and compounds eaten with magnesium-rich foods interfere and make absorption more difficult. One of these is phytic acid, a natural compound in many plant foods that can impair the absorption of magnesium along with other minerals, including calcium, zinc, and iron. Some nuts, seeds, legumes, and grains are high in phytic acid (levels can vary as much as 20x from one almond to another).
One way to mitigate impaired magnesium absorption is to eat foods rich in vitamin C (like citrus, red bell peppers, guava, and broccoli) when you’re eating foods high in phytic acid. It turns out that vitamin C essentially neutralizes phytic acid. One study found that 30 milligrams (the equivalent of less than half a cup of strawberries or broccoli, or ⅓ of a red pepper) was sufficient to eliminate phytic acid-related absorption issues.
In addition to consuming vitamin C-rich foods alongside food that are high in phytic acid, some other ways to boost your absorption of magnesium include:
- Reducing or avoiding calcium supplements at least two hours before or after eating
- Avoiding high-dose zinc supplements
- Getting enough vitamin D
- Eating some vegetables raw
- Eating sprouted, soaked, and fermented grains to reduce their inhibitory phytic acid content
- Not smoking
Should You Take a Magnesium Supplement?

The best way to get magnesium, as with most vitamins and minerals, is to eat foods that are rich in it.
If your blood levels are low, or you have some of the symptoms of magnesium deficiency, then you may also want to consider supplementation. But keep in mind that supplementation increases the risk of magnesium overdose, so it’s important to know the appropriate dosage and not take too much.
Magnesium Types
There are many types of magnesium supplements to choose from. Some of the most common include:
- Magnesium oxide is often prescribed (and is the form found in milk of magnesia). But this type of magnesium is more likely to cause diarrhea because higher doses are typically needed to have an impact. Furthermore, magnesium oxide only has an absorption rate of around 6%.
- Magnesium citrate (magnesium bound with citric acid) can have a laxative effect, which may help with constipation. It’s also often recommended for migraine prevention and is highly bioavailable.
- Magnesium glycinate contains the amino acid glycine, which works with brain neurotransmitters like GABA to promote calmness and improve sleep. It also has an anti-inflammatory effect, but doesn’t work as well for alleviating constipation.
- Magnesium gluconate treats magnesium deficiency. It appears to have the highest bioavailability among magnesium salts.
- Magnesium chloride is a magnesium salt combined with chlorine. It’s well-absorbed and often prescribed for heartburn, magnesium deficiency, and constipation.
- Magnesium lactate is a magnesium salt combined with lactic acid. It’s less common as an over-the-counter supplement than other forms of magnesium. It’s more commonly used to fortify foods and drinks. Still, supposedly gentler on the intestinal tract than some other forms, which can be helpful for people who require large doses.
- Magnesium malate contains malic acid, which is found naturally in fruits and wine. It has a higher absorption rate, which may be useful for treating magnesium deficiency. This form is common in the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome or fibromyalgia, although the jury is still out on its effectiveness.
- Magnesium taurate contains the amino acid taurine and may help regulate blood pressure and blood sugar levels. Its potential heart health benefits have primarily been observed in animal studies. So more research on human applications is needed.
Magnesium-Rich Recipes
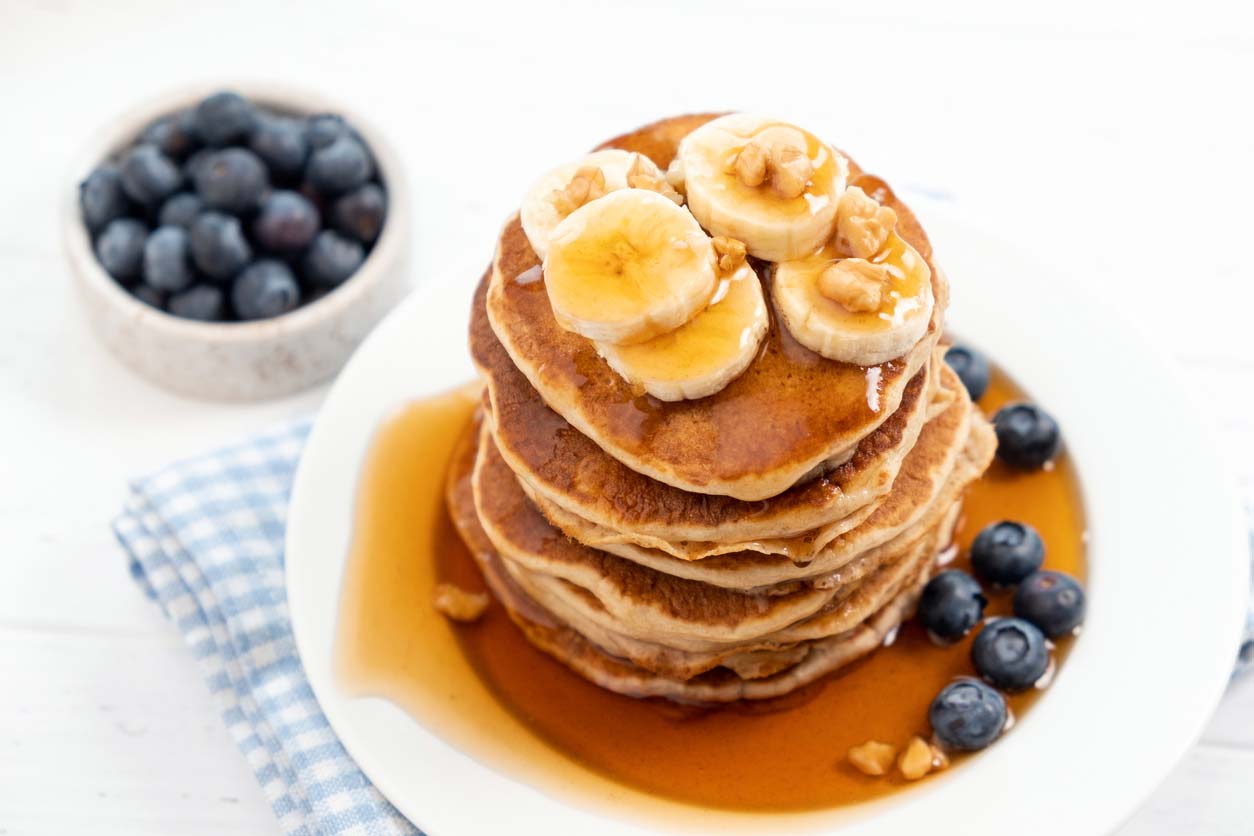

Whether or not you take a magnesium supplement, there’s little doubt about the health benefits of eating a magnesium-rich diet. You can boost intake throughout the day by incorporating magnesium-rich ingredients into your everyday cooking. The Blueberry Walnut Pancakes, Citrus Salad in a Jar, and Buffalo Cauliflower Tacos are just a few examples of nourishing recipes that contain ingredients high in magnesium, such as walnuts, oats, spinach, cashews, lentils, cauliflower and avocado (plus more!). To ensure you’re getting enough magnesium each and every day, consider adding extra magnesium-rich ingredients to a meal. Examples include sprinkling nuts or seeds to a grain bowl, slicing avocado into a sandwich, and tossing spinach into a stir-fry.
Blueberry Walnut Pancakes
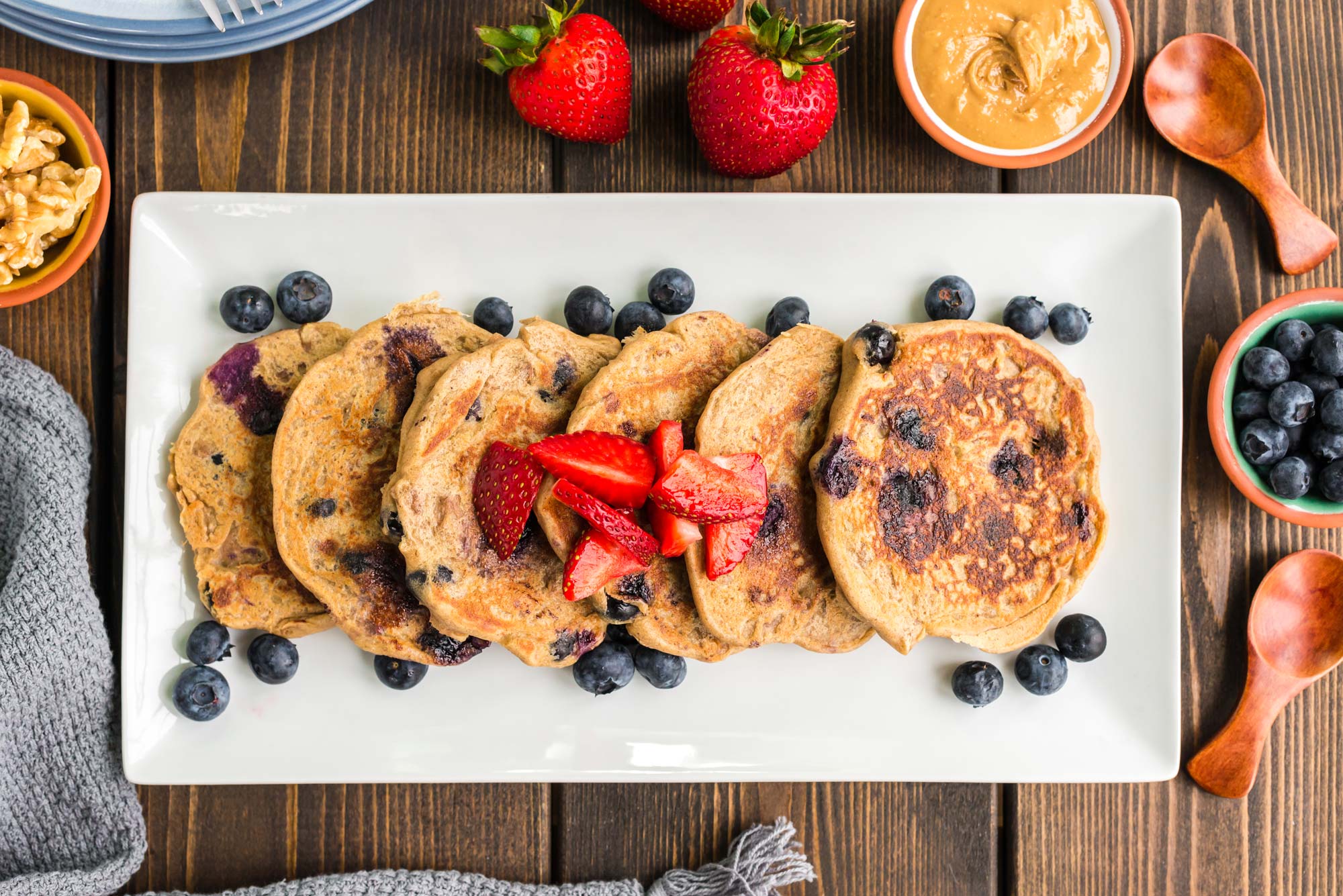

Walnuts, bananas, oats, and plant-based milk not only make these simple-to-create pancakes delicious, but they also provide a decent dose of magnesium to start the day. Add blueberries, or your favorite fruit, for a little added natural sweetness and even more plant-based nutrition.
Citrus Salad in a Jar
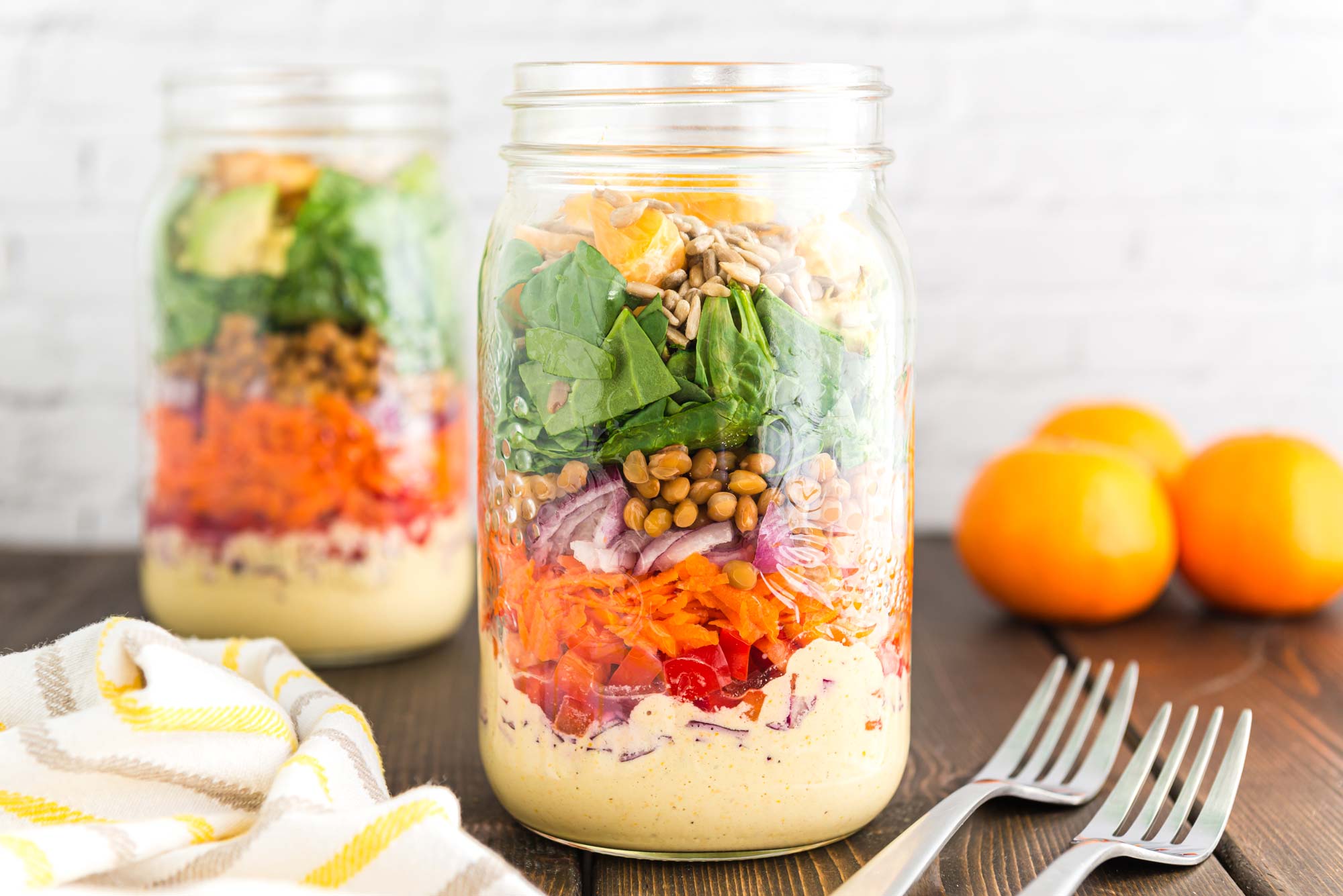

This salad checks all the boxes: crunch from the cashews, creamy from the avocado, sweet and savory from the dressing, and magnesium from just about all of the ingredients, including spinach, cashews, lentils, avocado, and sunflower seeds. Prepare the salad the night before work in a mason jar for a delicious and healing plant-powered lunch. Or add all of the ingredients directly into your favorite salad bowl for a tasty, impromptu, and nourishing meal.
Buffalo Cauliflower Tacos
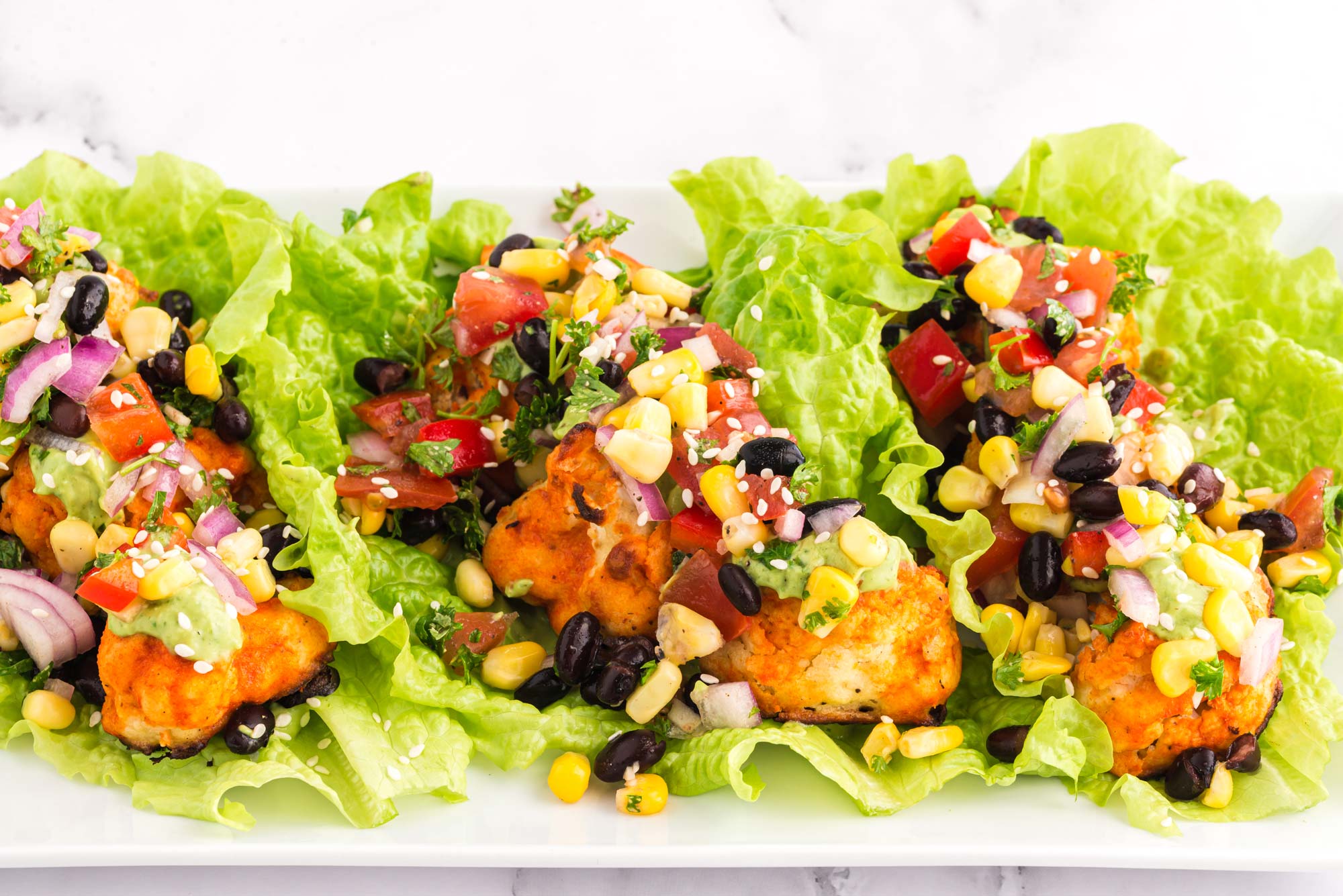

Who knew that tacos could be so healthy? The truth is there are countless ways to prepare tacos using plant-based ingredients. With so many filling options, you could create a different taco for every night of the week! This one, in particular, is pretty special with its high-magnesium ingredients, including cauliflower, avocado, black beans, and whole-grain tortillas. They may seem indulgent, but rest assured they’re providing your body exactly what it needs for bone, nerve, and heart health.
Magnesium Is Essential for Your Health

Magnesium is an essential mineral, necessary for many bodily systems to function properly. It has a number of health benefits, but most people don’t get enough of it. This contributes to a host of problems impacting heart, bone, sleep, and mental health. You can boost your levels through regularly eating magnesium-rich foods, optimising its absorption, and, if necessary, taking a low dose supplement.
Thanks Ocean Robbins, CEO of Food Revolution Network for the Article, August 2020.